Targeting B Cell malignancies? Raji-Luc is a model to test CD19-directed CAR-T cells and other novel approaches
作者:
马里兰·富兰克林,博士,科学发展副总裁
日期:
2017年6月
尽管CD19对人类B细胞癌的直接作用仍在研究中,但在大多数B细胞恶性肿瘤中发现了其表达。例如,急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)、B细胞淋巴瘤和B细胞白血病分别显示出80%、88%和100%的CD19表达。1 ALL表现为骨髓中淋巴母细胞的过度生成,这些细胞不断增殖,导致正常造血细胞的生成受到抑制。这些疾病在幼儿中更常见,但在老年人中也有发生。儿童的治愈率>80%,而成人的治愈率只有20-30%。一种类似的疾病是慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL),通常在老年人中诊断。ALL和CLL都被认为是适合CD19导向治疗的恶性肿瘤。虽然抗CD19单克隆抗体和其他方法正在被研究用于临床开发,但迄今为止最常见的靶向CD19相关恶性肿瘤的方法是嵌合抗原受体(CAR)修饰的T细胞(CAR-T)。CD19是第一个用于T细胞治疗策略的靶点,仍然是一个活跃的临床研究领域。
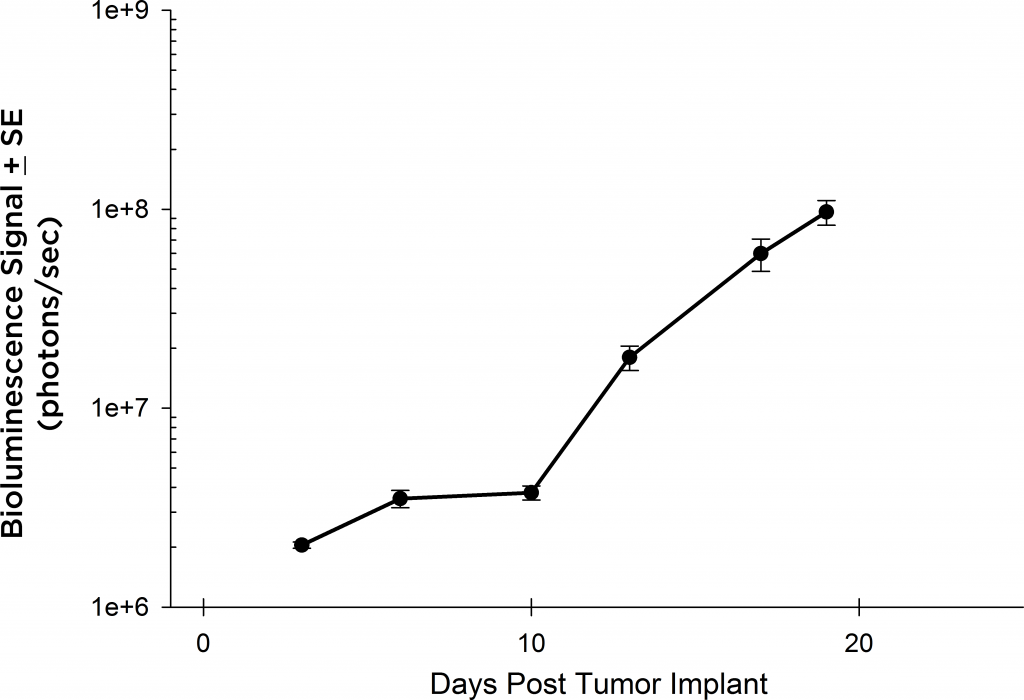
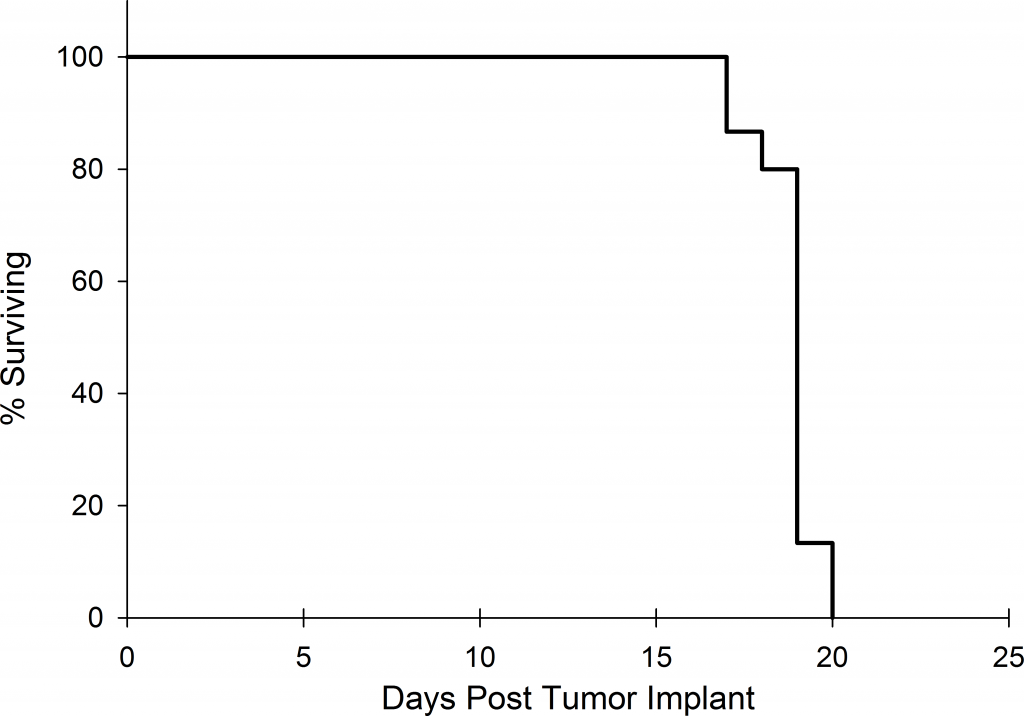
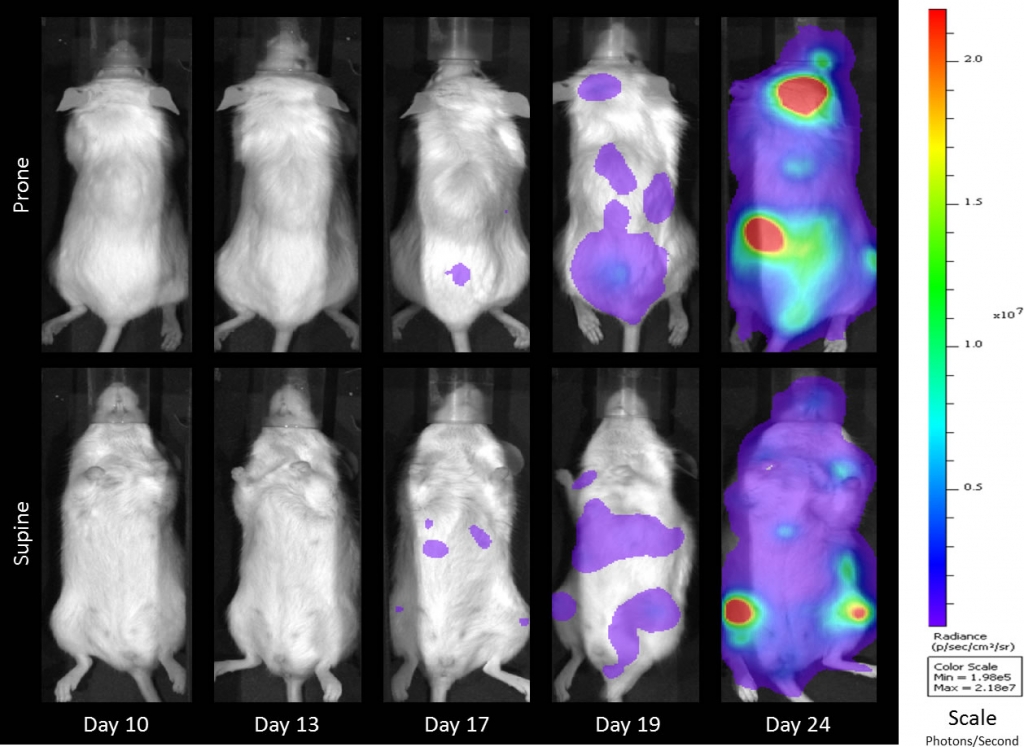
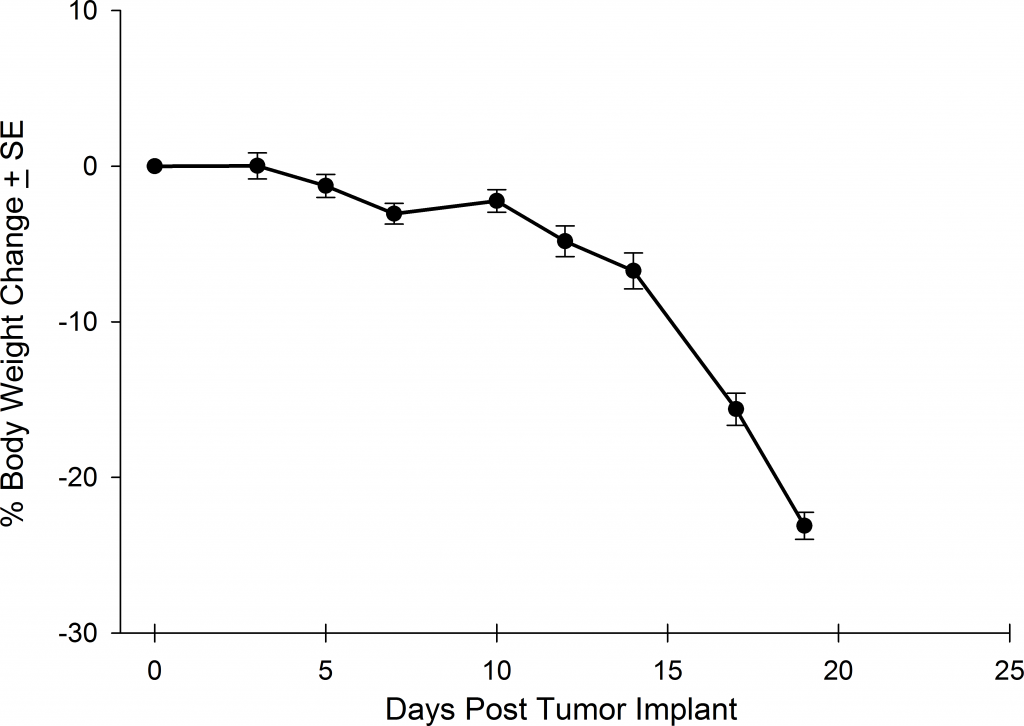
Preclinically, the human Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line Raji has been a mainstay for determining anti-tumor activity for approaches related to B cell malignancies. At Covance, we employ a luciferase-expressing Raji cell line (Raji-Luc) to allow us to track disease progression and therapeutic response over time throughin vivo光学成像。Raji-Luc是评价CD19介导的CAR-T治疗的优秀模型。我们已经在SCID和NSG小鼠中使用该模型进行了十多项CAR-T或其他细胞治疗研究。在许多情况下,免疫缺陷最严重的小鼠品系NSG是细胞治疗存活和持久性所必需的。因此,我们通过以下方法验证了Raji-Luc在NSG小鼠中的生长情况:in vivobioluminescence imaging (BLI) (figures 1A & B) and found an aggressive dissemination of disease as illustrated by an approximately 20 day overall survival (morbidity/mortality, figure 1C) endpoint. Consistent with the rapid induction of disease, the mice presented with progressive body weight loss (figure 1D) and ultimate hind-limb paralysis that required euthanasia.
Validation of Raji-Luc Growth in NSG Mice
Anti-tumor Activity of Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody—Rituximab
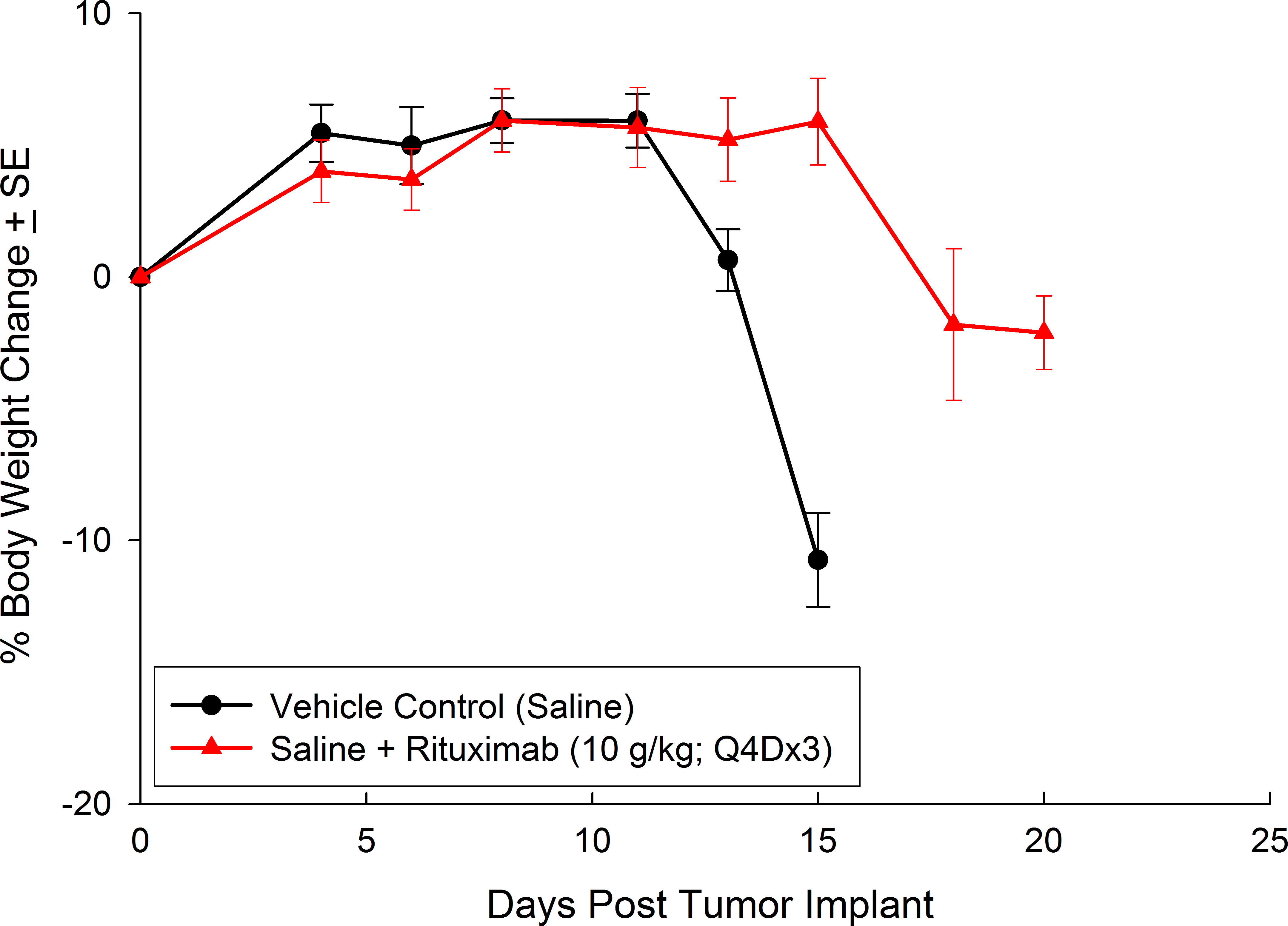
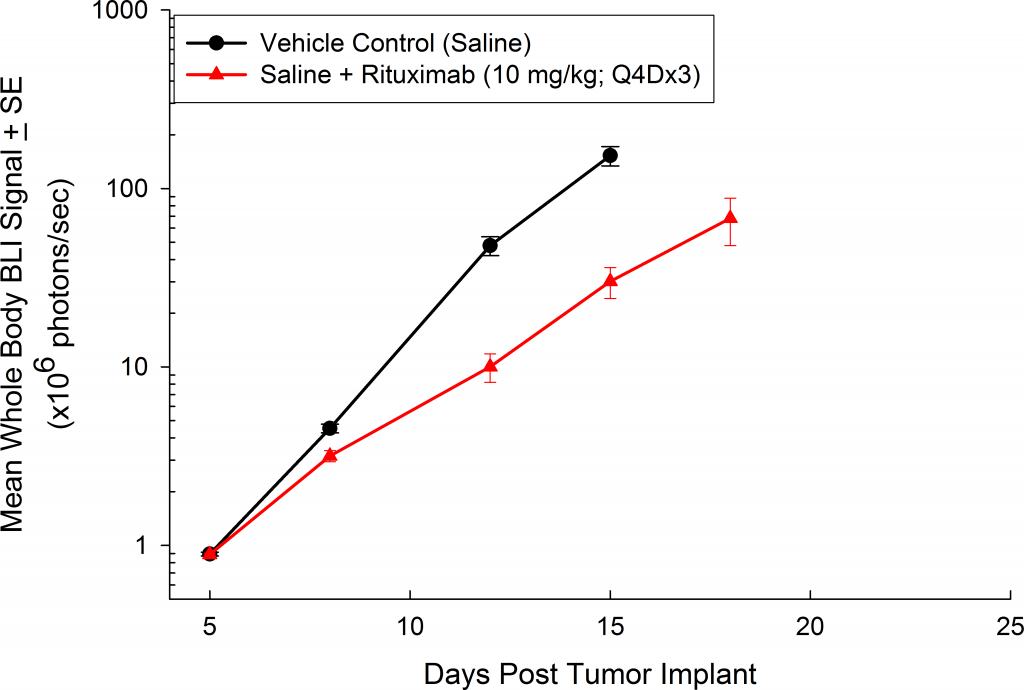
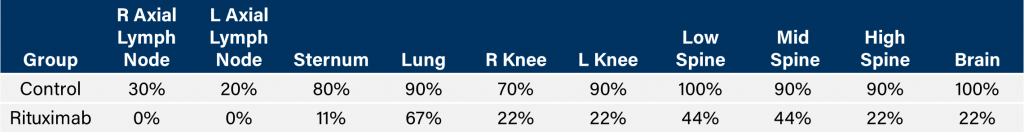
与CD19类似,CD20也是B细胞的标志物,也是治疗非霍奇金淋巴瘤等B细胞恶性肿瘤的药物的初始靶点。抗CD20单克隆抗体利妥昔单抗的临床开发为单克隆抗体作为肿瘤治疗药物的应用开辟了新的天地。在SCID小鼠中,我们测试了利妥昔单抗的抗肿瘤活性,并证明了总生存率的增加(图2A),这与通过以下方法确定的全身肿瘤负担的减少相关:in vivoBLI(图2B和2C)。与NSG小鼠的研究相似,我们观察到疾病进展的临床迹象,如后肢瘫痪和体重减轻(图2D)。除了in vivoBLI我们还检测了不同组织的疾病发生率ex vivoBLI (table 1). Throughex vivo此外,我们进一步证明利妥昔单抗治疗可降低总体疾病负担。

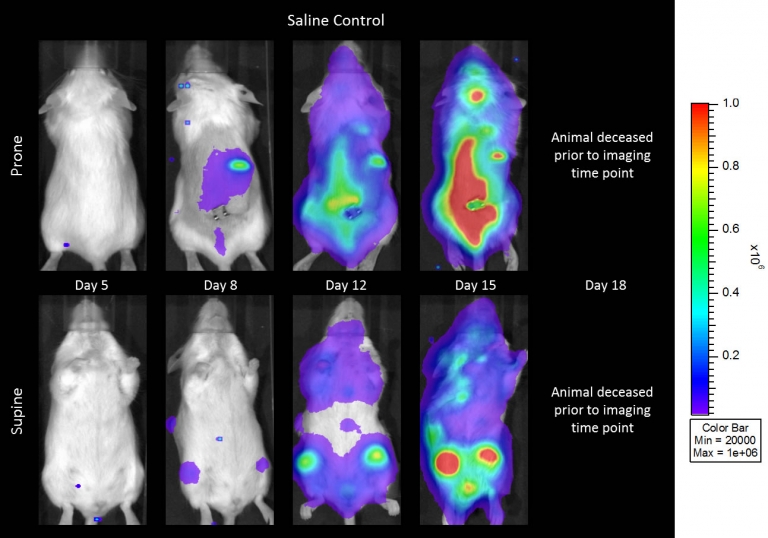
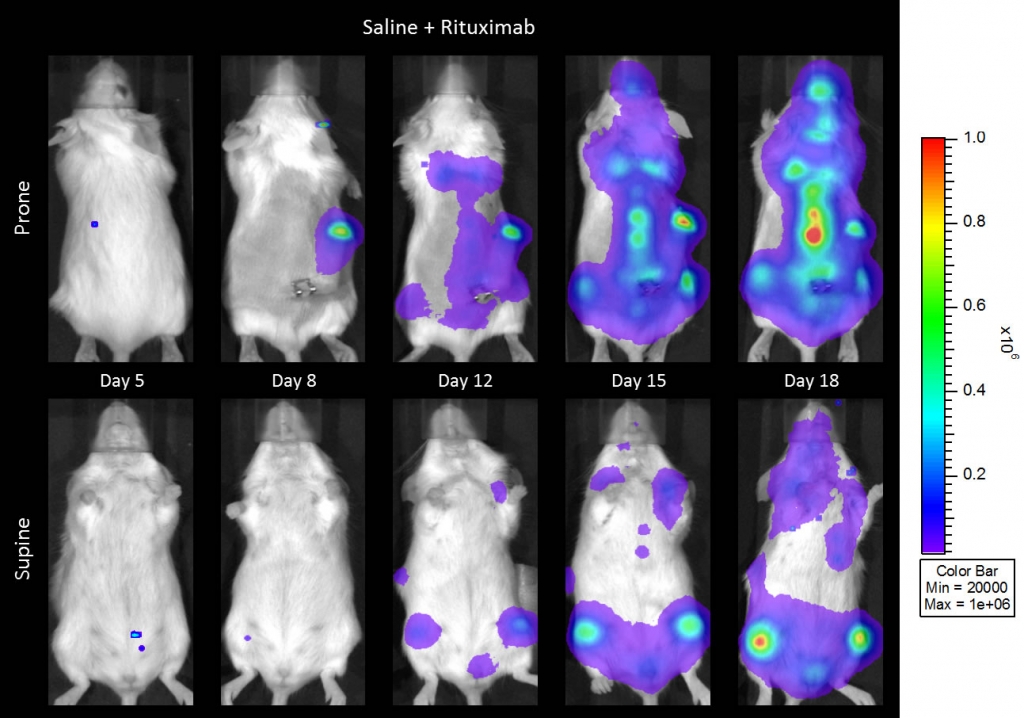
Raji-Luc模型在SCID小鼠皮下移植中的应用评价
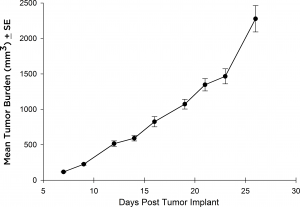
虽然大多数治疗方法在静脉注射后都采用Raji-Luc模型,但也有一些抗肿瘤策略需要皮下(SC)评估的情况。为此,我们在SCID小鼠的SC环境中验证了Raji-Luc系的生长。从植入到达到安乐死标准(图3),这条线的生长非常迅速,4天的倍增时间约为27天。
Thus, Raji-Luc in either the SCID or the NSG background provides a rapid model with which to test CD19 or CD20 directed therapies.
联系我们和我们的一位科学家谈谈拉吉·卢克或我们的其他模型如何用于你的下一个CAR-T研究。
1王,et al ., Exp。内科杂志。肿瘤防治杂志。2012;1:36.
Note: Studies were performed in accordance with applicable animal welfare regulations in an AAALAC-accredited facility