Modeling liver cancer with syngeneic hepa 1-6: an update
AUTHOR:
谢Barnes博士|导演,三英洁具tific Development
DATE:
November 2019
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) affects over one million people globally and is currently the third leading cause of cancer related deaths in the world.[1]在世界范围内,有800000名新诊断和700年,000 patient deaths each year. The incidence of HCC is highest in Southeast Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa due to high prevalence of hepatitis B and C viruses which strongly predisposes one to develop chronic liver disease and subsequent HCC.[1,2]In the United States, there are expected to be 42,030 new diagnoses and 31,780 patient deaths in 2019.[2]根据疾病的不同阶段,肝癌可以通过手术、化疗、靶向治疗和放疗进行治疗。[4]Current clinical trials are tackling unresectable or advanced stage HCC with mono or combination immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or oncolytic virus therapy.[1-4]These approaches have demonstrated tumor shrinkage and improved survival, but are not curative. Hence, there is a need for improved treatment options. Covance has developed the syngeneic HCC model, Hepa 1-6, for preclinical evaluation of immunomodulatory drug candidates.
Hepa 1-6 is a murine hepatoma derived from the BW7756 hepatoma that arose spontaneously in C57L/J mice, which contrasts with most available hepatoma models (BNL, A.7R.1, MH-129, MH134 and MH-22A) that are chemically transformed or induced lines. Therefore, the Hepa 1-6 tumor model established in immunocompetent mice represents a clinically relevant model for preclinical testing of immunotherapy.
Review of Earlier Data
在我们的2018 Hepa 1-6 Model Spotlight,我们介绍了模型的初始皮下生长和小但已建立的肿瘤(平均肿瘤体积约80-90mm)给药后的反应数据3). Treatment of Hepa 1-6 with checkpoint inhibitors体内was extremely effective against early stage disease, resulting in 50-100% durable complete responses, but leaving little room for improvement in combination with drug candidates. Throughout 2019, we have continued efforts to refine this model to enable checkpoint inhibition as a reasonable combination strategy with investigational drug candidates. Herein we present anti-tumor response data in a model of more advanced subcutaneous Hepa 1-6 disease.
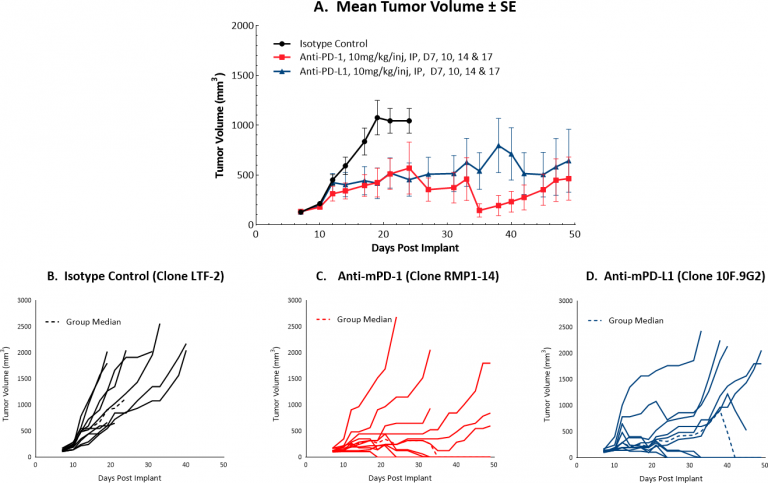
Checkpoint Blockade Response Data for Hepa 1-6
Initiating treatment with more advanced Hepa 1-6 tumors (at a mean tumor volume of ~130 mm3)结合检查站封锁,对候选药物的检测反应良好。图1显示了对照肿瘤和接受抗mPD-1或抗mPD-L1单药治疗的肿瘤的平均(A)和个体(B-D)生长。在肿瘤体积增加的情况下,每种单一疗法产生40%的持久完全应答,这表明虽然这种策略确实可以提供一种方法来测试合理的组合策略,但模型可能会进一步优化。我们将继续完善这个模型,以允许检查点封锁保持一个适度的反应,理想情况下较少的完整反应。平均肿瘤体积的微小差异可能意味着反应的巨大差异,因此我们正在系统地逐步探讨这一挑战,正在进行的一项研究测试了在平均肿瘤体积~150 mm处开始给药的检查点阻断的抗肿瘤疗效3. This study is not yet complete but is already indicating fewer complete responses compared to lower initiating tumor volumes (data not shown).
To further increase utility of this HCC model, we have luciferase-enabled the Hepa 1-6 cell line (Hepa 1-6-luc). This line is currently being optimized for use in orthotopic modeling of liver cancer. The luciferase tag will be used to monitor tumor progression by bioluminescence imaging (BLI) following an implant directly into the liver.
Advisement for Using the Hepa 1-6 Model in Your Next Liver Study
hep1-6模型为研究肝细胞癌提供了强有力的临床前手段。此外,结合流式yaboapp体育官网细胞术分析,对检查点抑制的强烈反应暗示了一个最小的免疫抑制肿瘤微环境,因此,Hepa 1-6模型可以被认为是免疫上“温暖的”。这种免疫上有利的表型对那些正在开发的治疗剂非常有吸引力刺激免疫系统。
拜托联系我们和我们的科学家谈谈Hepa 1-6或我们的另一个syngeneic modelscan be used for your next immuno-oncology study.
1Medavaram, S and Zhang Y, 2018. Emerging therapies in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Hematol Oncol 7:17.
2https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/liver-cancer/statistics
3Pinter M & Peck-Radosvljevic M. 2018. Review article: systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. Sep; 48(6): 598–609.
4Waidmann O. 2018. Recent developments with immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. Aug;18(8):905-910.
Note: Studies were performed in accordance with applicable animal welfare regulations in an AAALAC-accredited facility